What are my responsibilities as a CPHE?
Age Requirement
Ensure that pesticide handlers are at least 18 years old.
Safety Training
Before your employees begin handling pesticides or pesticide residues (handler activities), you must provide training about the risks of pesticide exposure, poisoning symptoms, first aid, and decontamination procedures. The training must be provided in a manner they can understand. Use a translator if necessary. A qualified trainer must be present to answer questions. This training must be provided every 12 months. When handlers request a copy of their training record(s) within two years of working with your organization, you must provide the training record(s) within two weeks.
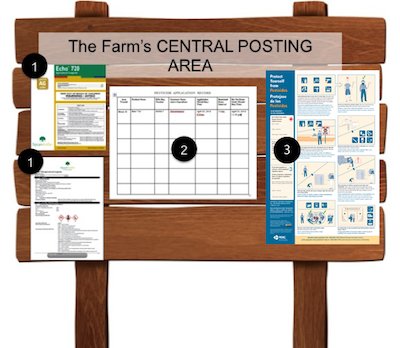
Establishment-Specific Information
Separate from the pesticide safety training, employers must tell workers and handlers where to find the safety data sheets (#1), pesticide application records (#2), pesticide safety poster or equivalent (#3), and decontamination supplies on each establishment where they perform work.
View More
View Less
Provide Information
- Inform handlers of entry restrictions and ensure those restrictions are followed.
- Inform handlers of all required label and application information. Ensure this information is accessible during the application and that it is understood by the handler.
- Provide training for safe use and maintenance of pesticide application equipment.
- Inform anyone who cleans or launders PPE of the following:
- The equipment may be contaminated with pesticides.
- Pesticides can have potentially harmful effects if you are exposed
- Instructions about how to properly clean PPE and how to protect themselves when handling such equipment
- Only allow trained and equipped handlers to repair, clean, or adjust pesticide equipment.
- If a person not employed by you cleans, repairs, or adjusts pesticide equipment, you must provide them certain information:
- The equipment may be contaminated with pesticides.
- Pesticides can have potentially harmful effects if you are exposed.
- Instructions about handling the equipment to limit pesticide exposure.
- Instructions about how to wash themselves and/or their clothing to remove and pesticide residues.
Provide Oversight
- Do not allow handlers to apply pesticides so that they contact anyone, either directly or through drift, other than trained and equipped handlers who are involved in the application(s).
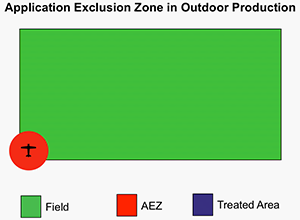
- Make sure handlers suspend applications if someone not involved in the pesticide application enters the Application Exclusion Zone (AEZ).
- When handlers are applying pesticides with a skull and crossbones symbol on the front panel, check-in with them at least every two hours. Text messages are not sufficient. You must be able to see or hear the handler every two hours.
- For fumigant or enclosed space applications, provide a second handler outside of the enclosed space to continually monitor the active handler. In addition, provide a second set of PPE in case there is a need to assist or rescue the handler making the application.
View More
View Less
Provide Personal Protective Equipment
- Supply any label-required Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), ensure its proper use, and provide proper care and disposal/replacement. Inspect PPE before each day of use. Shirts, pants, shoes, and socks are not considered “PPE” and you are not required to provide or maintain them. For more details about PPE requirements, see Chapter 4 of the HTC.
- When a respirator is required by pesticide labeling, you must provide the handler with a medical evaluation. This will ensure the handler is physically capable of wearing the respirator safely. You must also provide a fit-test to ensure the respirator fits properly and you must ensure handlers are trained in respirator use (within the last 12 months).
- Provide handlers with a pesticide-free area for storing personal clothing, and putting on and taking off PPE. You must also make sure handlers do not take contaminated PPE home.

Decontamination Supplies
- Provide water, soap, and single-use towels within a 1/4 mile of where pesticide handlers are working, or at the nearest vehicular access. They must also be supplied at any mixing/loading site, and in the location where handlers remove their personal protective equipment (PPE). At each site where decontamination supplies are required for handlers, you must also provide one set of clean coveralls. This is to be used in an emergency when the handler's clothing has become contaminated. Decontamination supplies must be kept outside the treated area or any area with an active REI.
- There must be three gallons of water per handler, measured at the start of the work period. Clean, running water meets the requirement. Otherwise, a tank of water may be provided.
- Hand-sanitizer is no substitute for soap and water because it doesn't wash the pesticide residue away. It rubs the pesticide residue into the skin.
- When handlers are mixing/loading pesticides that require eye protection, provide an eyewash station at the mixing/loading site or an equivalent amount of water. Acceptable eye-wash systems can supply 0.4 gallons/minute for 15 minutes, or 6 gallons of water in containers suitable for 15 minutes of gentle eye-flushing.
- When handlers are using pesticides that require eye protection, you must require them to carry at least one pint of water with them for emergency eye-flushing in the field.
View More
View Less
Information Exchange with Establishment Operators
When your business applies pesticides on someone else's property, you must provide the following information to the agricultural establishment operator:
- Location and description of area to be treated
- Date of application, with estimated start and end times
- Product name, EPA registration number, and active ingredient(s)
- Restricted-entry interval (REI)
- Whether the product label require verbal warnings, posted warning signs, or both
- All other safety requirements on the product labeling for workers and others.
Similarly, the establishment operator must provide the following information to you:
- The specific location and description of any treated areas on the establishment, including areas with an active REI, and
- Any restrictions on entering those areas. You must communicate those restrictions to your employees if they will be walking within 1/4 mile of the treated areas.
Emergency Assistance
In the event of a pesticide exposure, you must provide immediate transportation for handlers to a medical facility capable of emergency medical care. You must provide the Safety Data Sheet, product name, EPA registration number, and active ingredient(s) to the exposed employee(s) and medical personnel. Also, provide a description of how the pesticide was used and any circumstances that could have resulted in exposure to the pesticide.
No Retaliation
Do not retaliate against a pesticide handler who attempts to:
- comply with the WPS,
- file a complaint, or
- provide information in an investigation of alleged WPS noncompliance.

Regulatory Guidance
Browse brief guides about protections for workers and handlers, the AEZ, posting, PPE, exemptions, training, respirators, and more, in English and Spanish.
